I. Einleitung
According to survey data, the number of photovoltaic modules is expected to reach 8 million tons by 2030. What shocking numbers! However, traditional land-filling wastes valuable materials like glass, aluminum, copper, and silicon—while increasing environmental risks, therefore, how to dispose solar panels efficiently becomes a great challenge to human beings.

BSGH-Granulator provides a complete range of solar panel recycling systems, from small disassembly machines to fully automatic PV recycling plants, helping recyclers maximize recovery rates, reduce operating costs, and build sustainable businesses.
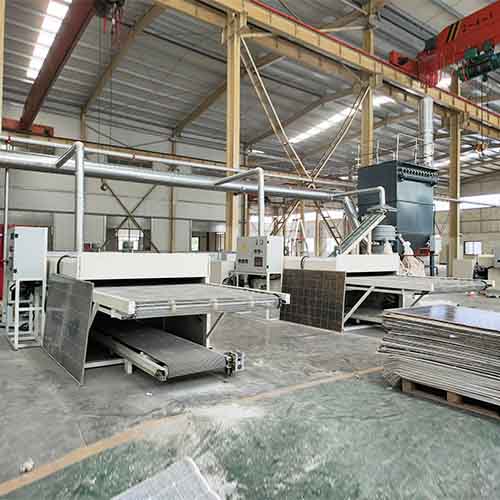
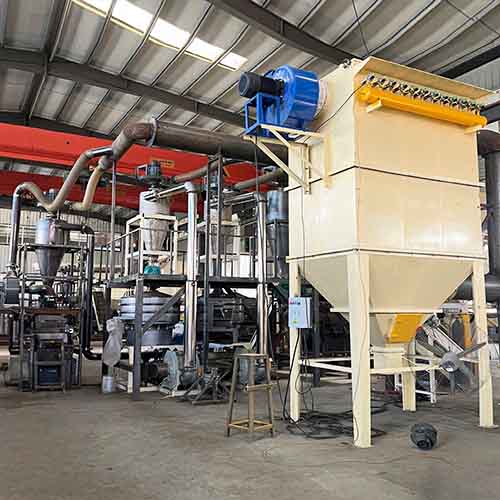



II. Are Solar Panels Recycled?
It is the first step to figure out what is PV solar made of then you can clearly check whether it can be recycled or not.
1. What Are Solar Panels Made Of?
Solar panels can be classified into two types: Silicon-Based PV Panels and Thin-film Based PV Panels which are mainly made of:
| Solar Panel Type | Silicon Based PV Panels | Thin-film Based PV Panels |
| Glass | 76% | 89% |
| Plastik | 10% | 4% |
| Aluminium | 8% | 6% |
| Silicon | 5% | / |
| Metalle | 1% | 1% |
2. Can Solar Panels Be Recycled?
Obviously, the answer is yes. With modern recycling systems, over 95% of solar panel materials can be recovered — making recycling both technically and economically viable. The process extracts valuable metals, glass, and silicon for reuse in new products. (Notes: Specifically check in the application part) According to the research, dismantling 100 pcs of scrap photovoltaic panels yields: silver 1 kg, copper 24 kg, silicon 70 kg, plastic 233 kg, aluminum 210 kg, and glass 1400 kg .
In summary, it is obvious that the composition and recyclable value of solar panels promote their development into an emerging industry.
III. Why Should We Recycle Solar Panels?
Solar panel recycling is essential — not only for its clear environmental advantages but also for the significant economic and industrial opportunities it unlocks.
1. Environmental Benefits
- Reduce landfill waste and prevent pollution
If solar panels are simply landfilled, heavy metals may seep into the soil and water sources, resulting in pollution. Recycling solar panels significantly reduces the volume of end-of-life panels sent to landfills and prevents potential soil and groundwater contamination.
- Recover valuable materials, reducing mining demand
Recovering high-purity glass, silicon, silver, and aluminum enables to conserve natural resources, creating a circular economy, turning waste into valuable resources so as to decrease the mining demand, beneficial for the ecosystem, meanwhile, ensuring solar power remains a truly clean energy solution from production to decommission.
- Lower the carbon emission of the solar industry
If PV panels are incinerated, components such as the plastic backsheet will produce carbon dioxide and other harmful gases. More importantly, mining primary silicon, silver, aluminum, and other ores requires massive investment in machinery, long-distance transportation, and complex smelting processes, all of which are accompanied by significant carbon emissions. Furthermore, efficient recycling can recover high-value materials (such as silicon, silver, and copper) and reuse them directly in the manufacture of new panels, thus greatly saving energy and carbon emissions. All in all, specialized solar panels recycling is capable of lowering the carbon release of solar industry.
2. Economic and Industrial Benefits
1) Create more job opportunities
The solar panel recycling industry chain can create diverse employment opportunities ranging from low-skill to high-skilled jobs, let’s break down:
- Front-end of the recycling chain: Deployment and logistics positions, such as: on-site assessment and dismantling technicians, reverse logistics specialists, and warehouse management & sorting operatives.
- Mid-end of the recycling chain: Core processing and technical positions, such as: production line operators, maintenance workers, process engineers, chemical recycling technicians, and health, safety & environmental specialists.
- Back-end of the recycling chain: Remanufacturing and innovation positions, including materials testing and certification engineers, remanufacturing engineers, and product designers.
- Support roles, such as: R&D scientists, software & data analysts, and policy & market development specialists.
2) Strengthen sustainable brand for manufacturers and EPC companies
For manufacturers and EPC companies, solar panel recycling is a core battleground for building next-generation sustainable brands. It’s more than just solving a potential waste problem, but a strategic move for:
- Continuous research on PV panels builds technological barriers, stabilizing supply chains, and elevating their brand.
- Exploring solar panel recycling can deepen customer relationships, differentiating services, and transforming from a “builder” to a “long-term energy asset management partner.”
Whoever solves the recycling problem first and effectively markets will build a solid brand in the increasingly photovoltaic market.
In a word, solar panel recycling enables to provide both environmental and economic benefits which makes it a rising but competitive field.
IV. How to Recycle Solar Panels: A Step-by-Step Process
It is not a simple task to recycling solar panels but requires specialized procedures and professional equipment to obtain great-value final products so that you can get higher returns while be good for eco-system. Here’s the specific steps for your reference:
Step 1: Collection – Establishing Collection Points
- Centralized: Partner with large power plant owners and operation & maintenance companies to set up temporary collection boxes at project sites.
- Distributed: Cooperate with distributors and installers to establish a retail collection network targeting the residential market.
- Reverse Logistics: Design efficient transportation routes to centralize scattered used components at recycling plants.
Step 2 – Initial Inspection and Sorting
1. Visual Inspection:
- Inspect the panels for integrity and any obvious physical damage, hot spots, aging, etc.
- Identify panels with fire damage or damp mold; these may require special handling.
2. Technical Testing:
Use a portable IV tester to quickly assess the panel’s power generation performance.
3. Classification and Processing:
- Reusable: Early-retired panels with acceptable performance (typically >80% of initial power) can be refurbished and used in the secondary market where performance requirements are not high.
- Recyclable: Panels with severely degraded performance enter the recycling line.
- Disposal: Severely damaged panels (e.g., fire, cracked) may require direct safe disposal.
4. Sorting by Types:
Separate crystalline silicon panels from thin-film panels (e.g., cadmium telluride, copper indium gallium selenide) because their recycling processes and extracted materials are completely different.
Step 3 – Disassembly and Pre-processing
1. Removing the Aluminum Frames
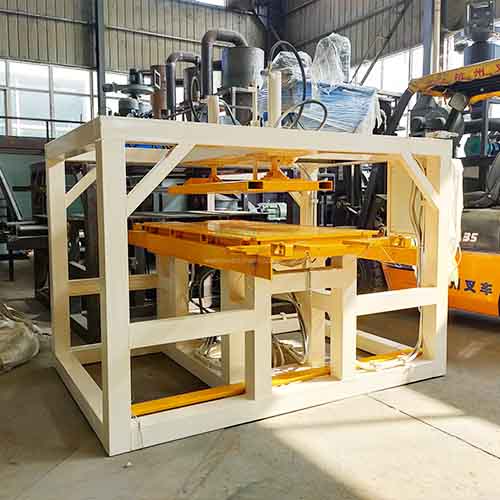
Using our automated aluminum frame removal machine to obtain high-purity aluminum, which can be directly melted down or reused to manufacture new frames, resulting in high closed-loop value.
2. Dismantling the Junction Box:
Separate the junction box from the back panel by cutting or heating, you will gain a mixture containing copper cables and plastic, which can be sent to the corresponding copper and plastic recycling streams.
Step 4 – Separation and Material Extraction
1. Glass Separation
The glass removal is the core technology and value of the entire recycling process, aiming to separate glass, EVA encapsulation film, and solar cells.
BSGH-Granulator solar panel glass removal machine via pyrolysis method can yield 100% pure glass granules and EVA backsheet, currently the most mature and widely used industrial method.
2. High Value Mixture
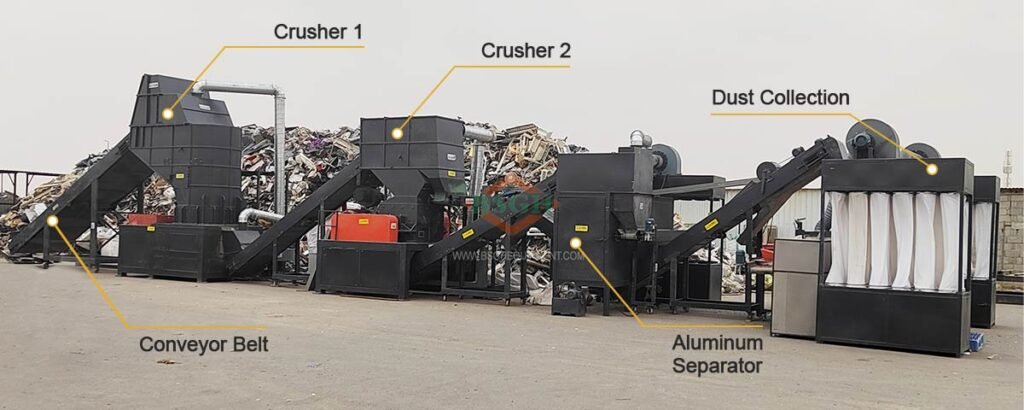
After removing its aluminium frame and glass layer, our solar panel recycling plant – an integrate crushing and separation system including shredding, crushing and grinding with vibrating screen and air separation, capable of achieving pure copper, plastics and silver & silicon mixture.
3. Further Extraction
The silicon-silver mixture is separated by acid leaching and refining to obtain metallurgical-grade pure silicon and high-purity silver.
By following the steps outlined above and continuously innovating technologically, the solar energy industry can not only overcome its environmental challenges but also transform waste into “urban mines,” truly solidifying its position as a cornerstone of sustainable energy solutions.
V. Applications of Recycled Materials from PV Panels
When recycle a solar panel, we’re not just disposing of waste — but unlocking a treasure of valuable materials. Through advanced recycling processes, over 95% materials can be recovered and given a new purpose. Here’s a look at where these key materials end up and how they circulate in the ecosystem.
1. Glass: The Clear Leader in Recycled Content
The vast majority of a solar panel is glass, and it’s one of the easiest materials to reclaim, can be used in
- New Solar Panel: After cleaning and remelting directly into the manufacturing of new solar glass, reducing the need for raw materials and energy.
- Building & Insulation Materials: Transformed into other industrial products like fiberglass insulation (glass wool) or incorporated into ceramics and construction aggregates.
- Everyday Glass Goods: The purified cullet is a valuable feedstock for producing new bottles and jars.
2. Precious & Base Metals: Silver & Copper
The conductive metals within solar cells are highly valuable and are carefully extracted for reuse.
- Silver: Refined to a high purity and can be directly back into the supply chain. It’s most commonly used in new solar cells or for other high-end applications like electronics and jewelry.
- Copper: Because of excellent conductive properties and utilized in electric vehicle (EV) motor coils, new electrical cables, and a wide range of consumer electronics.
3. Silicon: The High-Tech Heart of a Panel
The silicon wafers are another high-value resource and can be applied in:
- New Solar Ingots & Wafers: Remanufactured into new high-purity ingots and wafers, creating a true circular loop for the solar industry.
- The Electronics Industry: Serves as a prime feedstock for manufacturing various silicon-based components in the tech sector.
- Metallurgical Applications: Used as a valuable additive in the production of aluminum and other metal alloys.
4. Plastics: EVA & Backsheet Recovery
The plastic from encapsulant (EVA) and backsheet provides sustainable ways for:
- Low-Grade Plastic Products: Ideal for manufacturing durable, low-grade plastic goods such as shipping pallets or plastic lumber.
- Waste-to-Energy (WtE): Can be processed into Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF): a high-calorific-value alternative to fossil fuels, used for energy recovery in cement kilns and industrial power plants, effectively turning waste into a power source.
By understanding the full lifecycle of these materials, we can appreciate how solar panel recycling isn’t just a recycling solution — it’s also a critical link in building a sustainable future.
VI. Future Outlook – Smarter Design, Easier Recycling
The solar recycling industry is evolving rapidly, mainly lies in:
- Panels with valuable materials to recover
- Government EPR regulations mandate recycling plans
- New solar recycling plants are emerging across the U.S., Europe, and Asia
- Automation and AI sorting systems improve recovery efficiency
As recycling technology advances, solar waste will transform into valuable resources, powering a truly circular green economy.
VII. Conclusion
Solar panel recycling is not only an environmental necessity but also an opportunity to transform waste into treasure, making profits at the same time.
Bei BSGH-Granulator, we provide solar panel recycling machines that provide high recovery rates, low power consumption, and flexible configurations for different plant capacities.
Contact us today to learn how our advanced solar panel recycling solutions can help you build a cleaner, greener solar future.
VIII. FAQ
Q: Can I throw my solar panel in the trash?
A: No. Panels must be handled as electronic waste and recycled by certified facilities.
Q: Will recyclers pay for old panels?
A: Some may, depending on condition and material composition.
Q: How long do solar panels last?
A: Typically 25–35 years, depending on maintenance and environment.
Q: Can broken panels be recycled?
A: Yes. Glass, metals, and silicon can still be recovered efficiently.