There are more than 64 kinds of non-ferrous metals, and some common include aluminum, copper, lead, nickel, tin, titanium, and zinc. These metals are common used in our daily life and do not contain iron and have unique properties that make them valuable in various applications. So, now you’re probably wondering where do we typically use those metals?
What Are Non-Ferrous Metals?
Non-ferrous metals refer to all metals except iron, manganese, and chromium. Most have special properties: like being resistant to rust and easy to shape. They are widely used in everything from electronics to construction.
Let’s dive deeper. You may be curious about the common types of non-ferrous metals we used in our life, so I will give you some examples:
List of Non-Ferrous Metals



Alumínio
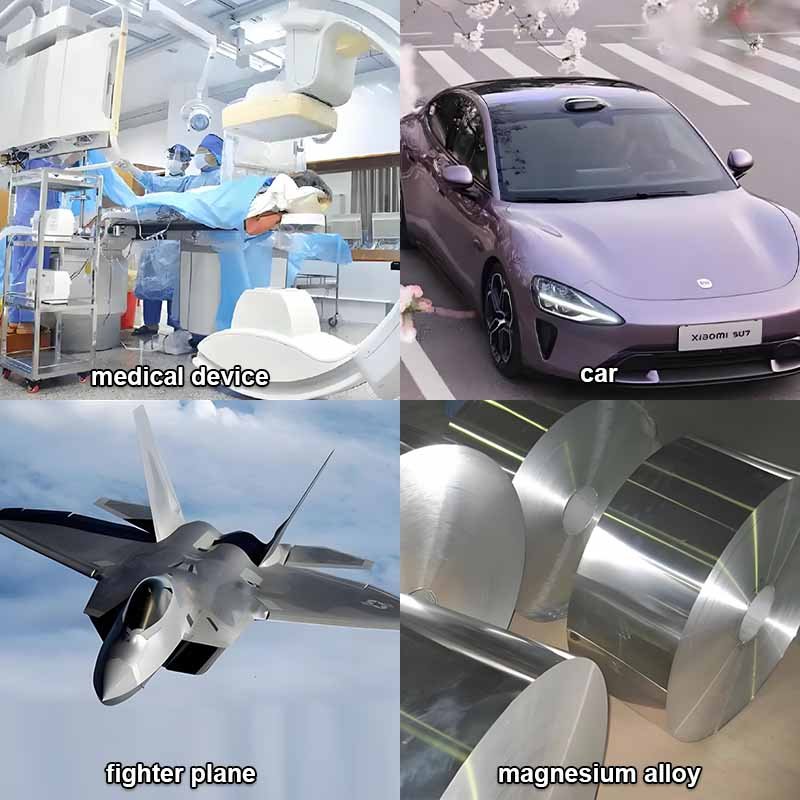
This metal is lightweight and low-melting, so you often see it in airplanes, cars, and cans.
Cobre
Copper is great at conducting electricity. That’s why we use it in wires and electronics.
Liderar
Lead is dense and resistant to corrosion. People commonly use it in batteries and as a shield against radiation.
Nickel:
Nickel is strong and resists corrosion too, often used in alloys like stainless steel.
Estanho
Tin is soft and protects other metals from corrosion. It’s often used as a coating for food cans.
Titanium
Titanium is super strong but lightweight. You’ll find it in aerospace, medical implants, and sports equipment.
Zinco
Zinc resists corrosion, which is why it’s used to protect steel in galvanization.
These metals have unique properties that make them useful in many different fields.
They don’t rust like iron, so they can exist longer in certain environments. They are also easy to shape and work with, which makes them ideal for various manufacturing processes. Understanding these metals helps hunman-beings to upgrade technic and produce more useful items.
Features and Application of Non-ferrous Metals
We can classify non-ferrous metals based on their physical properties, such as conductivity. Copper, gold, and aluminum are excellent conductors, making them ideal for wires and electrical appliances. The chemical properties like corrosion resistance make brass and stainless steel useful in harsh environments. Even biological properties play a role, as metals like titanium are compatible with biological structures, useful for biological scaffolds.
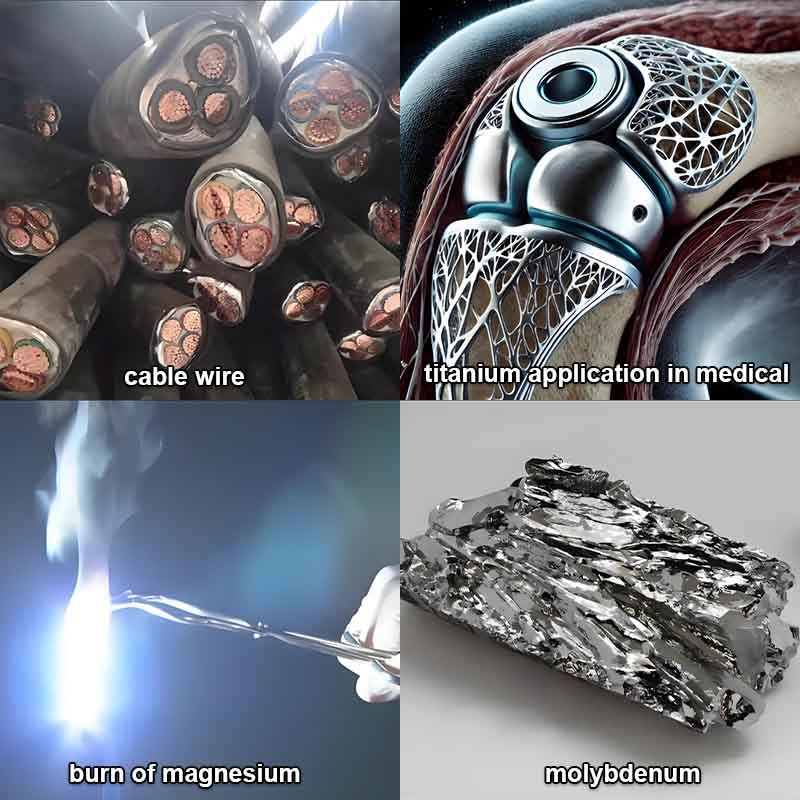

Digging deeper into the different classifications, let’s see some typical application scenarios.
Physical Properties
Some metals excel at conducting electricity. Copper, gold, and aluminum are great examples. You’ll find them in wires, cables, motors, and various electrical appliances.
Others conduct heat well. Such as copper and aluminum in heaters and pots. Aluminum alloys have got you covered for that. Of course, some metals, like gold and silver, are just valuable. Sometimes they can replace the cash to trade.
Chemical Properties
Some metals can burn, like magnesium. This makes them ideal for incendiary bombs and illumination flares. And some have reductive properties, which are essential for batteries. Lithium and sodium are common use in this aspect. And then there’s corrosion resistance. Brass and stainless steel are very good at it, so we use them in environments where other metals would rust.
Biological Properties
Some metals integrate well with biological structures. Calcium, sodium, and potassium are essential in medicine for this reason. A few metals are compatible with biological structures. This makes them ideal for biological scaffolds, like titanium, always be used in people healthy.
Rare Properties
Certain metals have rare properties. We often combine them with other metals to create high-strength alloys. Tungsten, molybdenum, and titanium are often used for this purpose.
Understanding these properties helps us choose the right metal for the job, leading to better and more efficient products.
Why are Non-Ferrous Metals Important?
Non-ferrous metals play a bigger role in our lives than we often realize. From the copper wiring that keeps our homes powered to the aluminum in our cars and smartphones, these metals are everywhere. They help create stronger, lighter, and more durable products across industries. They also drive innovation—powering the tech we rely on and enabling next-generation systems. Even in national defense, non-ferrous metals are essential, forming the backbone of advanced equipment and weaponry. Simply put, they’re vital to the way we live, work, and protect our future.

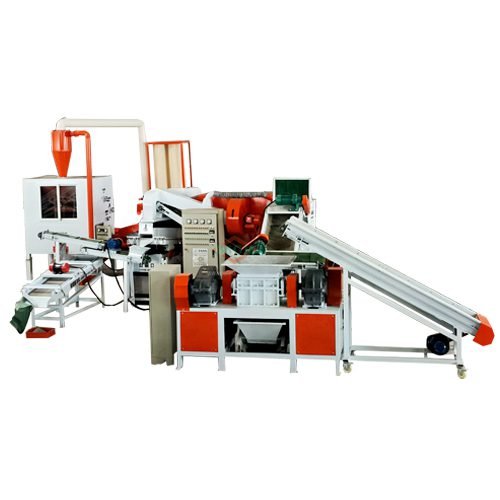
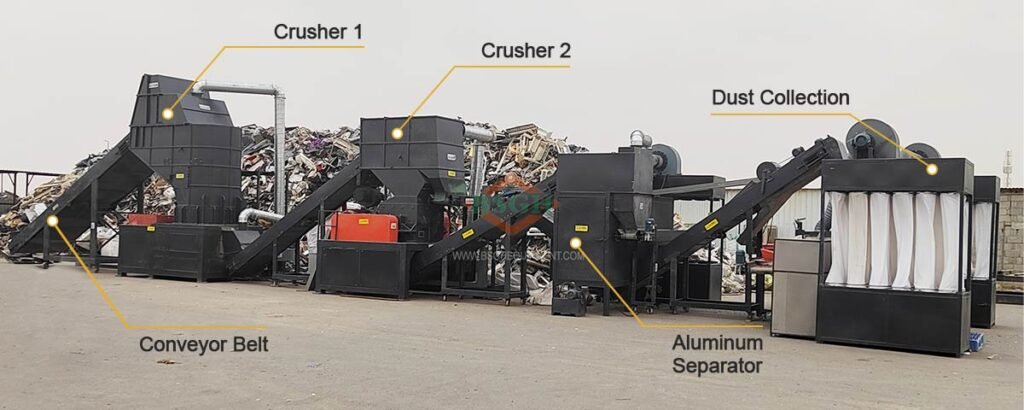
How BSGH Granulator Recycle Non-Ferrous Metals?
BSGH Granulator uses ferrous metals and non-ferrous metals to make durable and efficient recycling machines. Copper wire granulator plants, máquinas de decapagem de cabos, máquinas de reciclagem de radiadores, máquinas de reciclagem de motores e trituradores all benefit from alloys that give them better durable property and wear resistance.
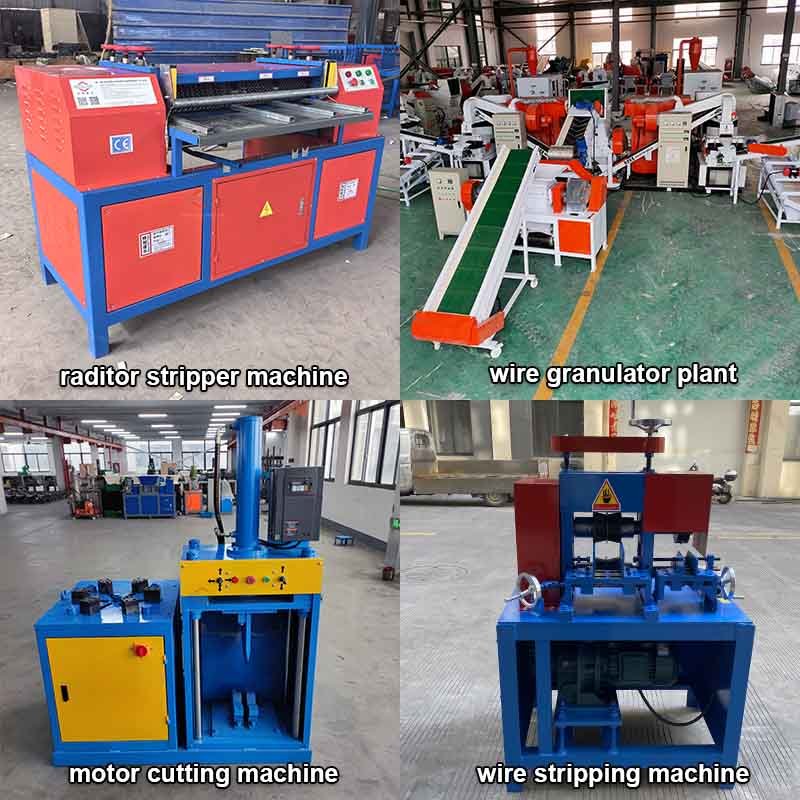

Our company also uses non-ferrous metals combined with ferrous metals to create some excellent alloy blades that are equipped in our machines. For example:
- our copper wire granulator machine efficiently separates copper from wires.
- Our cable stripping machine quickly removes the insulation from cables.
- Our radiator recycling machine processes radiators to efficiently get pure copper efficiently.
- Our motor recycling machine extracts copper windings from electric motors.
- Our shredders break down large pieces of metal into smaller, more manageable sizes.
Conclusão
Non-ferrous metals have amazing properties and deserve thorough research. Alloys made by combining metals offer excellent performance which will be a chance for every company to make efforts . Like BSGH provides professional technical support for recycling these valuable materials, and has make a great success.